The mildest form of varicose veins, known as spider veins, may not require a doctor’s care. However, as vein disease progresses, you may need treatment to relieve the resulting discomfort, redness, swelling, and ulcers. Consider how vein disease progresses and the best options for treating varicose veins at home or with a doctor’s help.
The Progression of Vein Disease
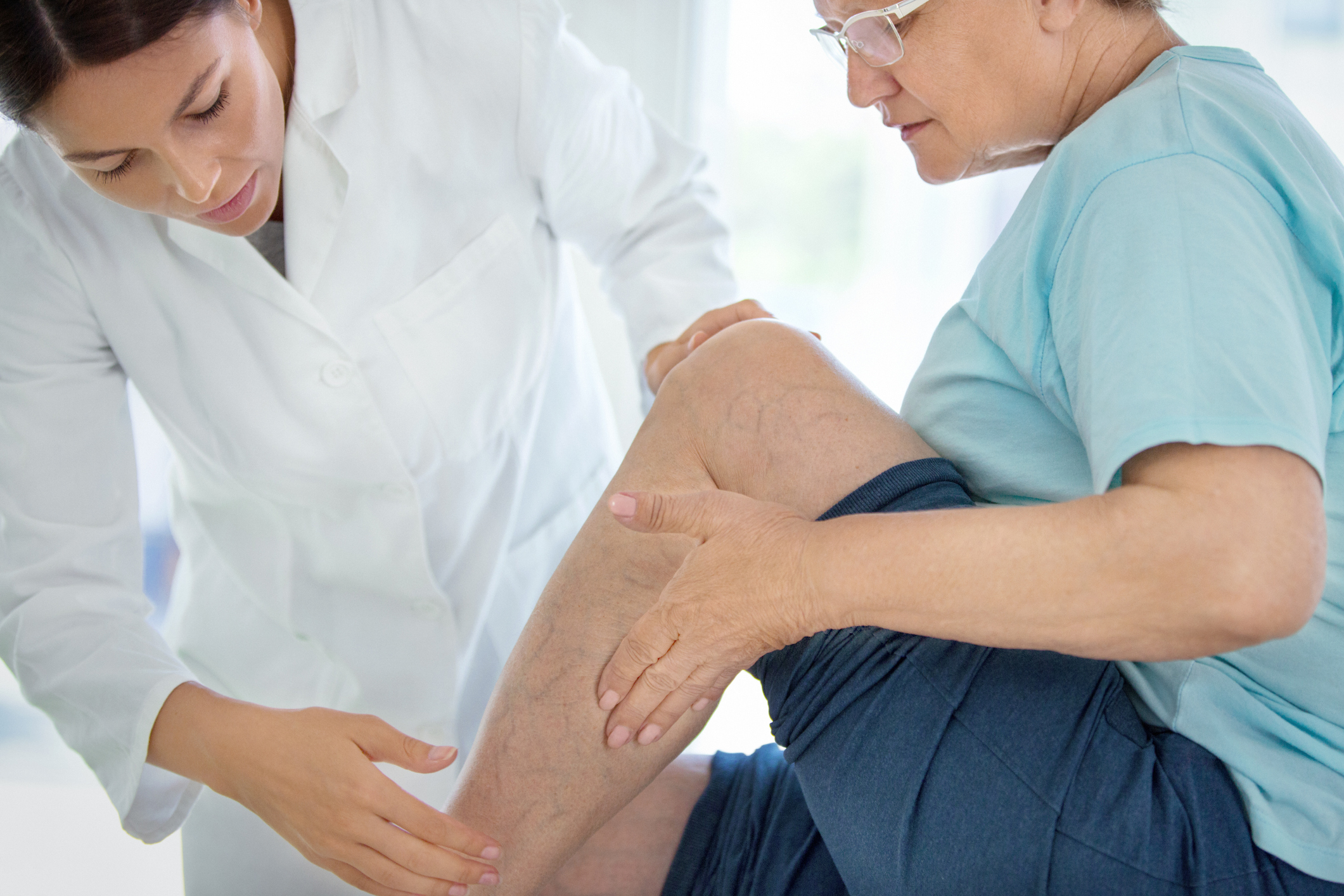
Stage 1: The first stage of vein disease is called spider veins. When these first develop, you may notice the appearance of dilated skin capillaries just under the skin. These create a spider-like appearance, but they usually cause no further symptoms.
Stage 2: If spider veins progress to varicose veins, they become rope-like and bulge from the surface of your skin. This is the stage of vein disease when you may begin to experience achy, tender, and sore legs, which may interfere with your day-to-day life.
Stage 3: Left unaddressed, varicose veins may evolve into other health problems, such as leg edema. This condition is characterized by chronic swelling that worsens as the day goes by and after standing for long periods. At this stage, some people also experience restless leg syndrome, itchy skin, and leg cramps.
Stage 4: Over time, vein disease can lead to skin changes, including discoloration and thinning of the epidermis. It may begin to appear as though you have brown stains on your skin, which occurs as blood leaks from your blood vessels into the surrounding soft tissue.
Stage 5: In the final stage of vein disease, leg ulcers develop. These may be extremely painful and itchy, requiring constant care and dressing to avoid infection.
At-Home Treatments for Varicose Veins
In the early stages of vein disease, you may not be too concerned if you’re not in any pain. However, even if there’s no discomfort, you shouldn’t ignore superficial spider veins and newly developing varicose veins. Prompt care may improve their appearance, but what’s more, at-home treatment can prevent the progression of vein disease. Here’s what you can do without additional assistance from a doctor.
Wear Compression Stockings
You can find over-the-counter stockings at a pharmacy or medical supply store. Expect mild to moderate compression from these products. Higher pressure stockings require a prescription. The purpose of compression stockings is to help your muscles push blood up your leg. They provide the most compression at the ankles and gradually decrease in pressure the higher up your leg they go.
Put on your compression stockings in the morning before getting out of bed. While lying on your back, raise your legs into the air and pull the stockings on evenly. Wear them all day, if possible. Also, take breaks from your daily activities to elevate your legs for 10 to 15 minutes several times a day.
Take OTC Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Aspirin and ibuprofen are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) designed to reduce inflammation and treat mild to moderate pain. You can take these over-the-counter medications with or without wearing compression stockings.
Medical Procedures for Varicose Veins
At-home care is often enough to prevent spider veins from getting any worse. Still, you should contact a doctor immediately if you notice the skin around a varicose vein becoming discolored or ulcerated. You may also need medical treatment if you experience vein-related leg pain, even if there are no obvious outward symptoms.
The goal is to treat your vein condition with the least invasive procedure possible. Consider your options.
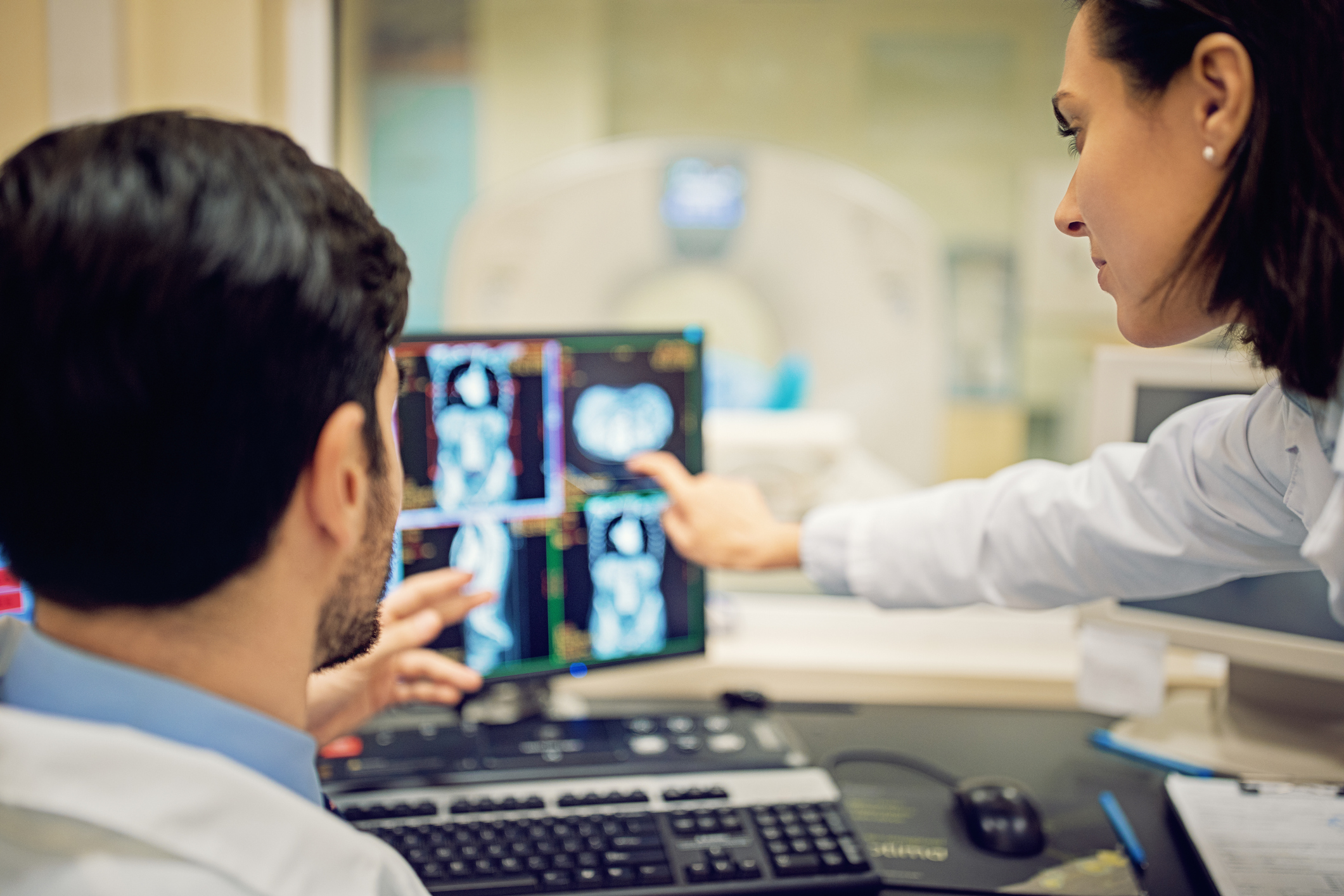
Interventional Radiology
This minimally invasive treatment is an alternative to open surgery. It involves placing a catheter inside the body with the aid of image-guided technology, such as CT scans, X-rays, or MRIs. Heat is then applied with radiofrequency waves or lasers to destroy and ultimately close the varicose vein.
Laser Treatment
This medical procedure is usually performed on small varicose veins. It involves directing light energy from a laser at a bulging vein, causing it to gradually fade and disappear. Multiple treatments may be needed to see the final results.
Sclerotherapy
Small to medium-sized varicose veins may be treated with sclerotherapy. This chemical treatment involves injecting material into the affected vein, causing it to harden and shrink so it can no longer transport blood.
Surgery
As a last resort, surgical removal—also known as ligation and stripping—may be used to treat large varicose veins that have advanced past the early stages of vein disease. Be aware that surgery may leave tiny scars behind.
Schedule a Free Vein Screening in Salem, OR
Salem Radiology Consultants is proud to be the largest radiology group in the Salem, Oregon area. Our depth of specialization ranks among the services you would expect to find at major university medical centers. If you’re concerned about bulging, uncomfortable veins in your legs, we can help. Contact us at (503) 399-1262 to schedule a free vein screening at our clinic today.